The flicker of the terminal screen was my only companion as the server logs spewed forth an anomaly. Something that shouldn't be there. In the shadowy corners of the network, the unpatched, the misconfigured, and the frankly forgotten systems whisper their secrets. Today, we're not just mapping ports; we're hunting for weaknesses. We're talking about Nmap, but not the Nmap you learned in your first week. We're diving deep into its vulnerability scanning capabilities, turning its packet-crafting prowess into an offensive analyst's keen eye.
Nmap, the Network Mapper, is often reduced to a glorified port scanner. A digital crowbar to rattle some doors. But for those who understand its architecture, its extensibility through the Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE), it becomes a formidable tool for reconnaissance and vulnerability identification. Forget the static lists of open ports; we're talking about identifying exploitable services, outdated software versions, and even potential configuration flaws that could be the crack in the perfect facade.
The Evolution of Nmap: From Discovery to Detection
Nmap's journey from a simple host discovery tool to a sophisticated vulnerability scanner is a testament to its open-source nature and the ingenuity of its community. While its core function remains network discovery – identifying live hosts, open ports, and listening services – the advent of NSE scripts revolutionized its utility. These scripts, written primarily in Lua, allow Nmap to perform a wide array of tasks beyond basic scanning, including vulnerability detection.
When we talk about vulnerability scanning with Nmap, we're primarily referring to the execution of NSE scripts specifically designed for this purpose. These scripts query services for known vulnerabilities, check for default credentials, identify specific software versions susceptible to known exploits, and even attempt to discover certain types of misconfigurations. It’s about making Nmap work smarter, not just harder.
For any serious penetration tester or network defender, mastering these advanced Nmap techniques is not optional; it's fundamental. While commercial vulnerability scanners exist, Nmap offers unparalleled flexibility, customization, and, crucially, a deep understanding of the underlying network protocols. Knowing how Nmap achieves its results empowers you to interpret them accurately and to adapt your approach when facing novel systems.
"The security of your network is only as strong as your weakest link. And often, that link is a service you didn't even know was exposed or vulnerable."
Understanding Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE) for Vulnerability Analysis
The heart of Nmap's vulnerability scanning power lies in the Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE). NSE enables users to share, download, and run scripts to automate a wide variety of networking tasks. These scripts have access to Nmap's extensive databases of host information, service probes, and operating system detection capabilities. When you invoke NSE scripts, you're essentially telling Nmap to perform more complex interactions with the target hosts.
NSE scripts are categorized by their function. For vulnerability analysis, we're primarily interested in scripts that fall under categories like vuln (vulnerability detection) and exploit (scripts that attempt to exploit vulnerabilities).
To list available scripts, you can use:
nmap --script helpTo see scripts specifically in the 'vuln' category:
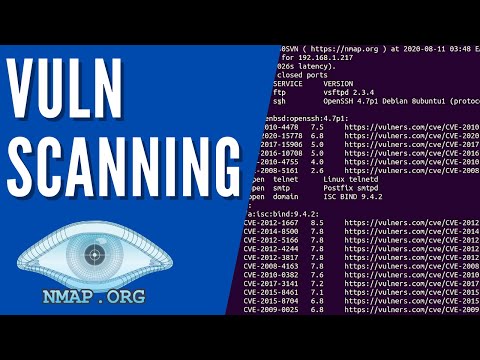
nmap --script help vulnThis is where the real magic happens. Instead of just a list of open ports, you can get detailed information about potential weaknesses. For instance, a script might detect an outdated version of Apache with a known remote code execution vulnerability, or a default credential on a database service.
Taller Práctico: Executing Vulnerability Scans with Nmap
Let's get our hands dirty. We'll simulate a common scenario: scanning a target network for known vulnerabilities. For this exercise, we assume you have a controlled lab environment or explicit permission to scan the target systems. Never scan systems without authorization; the consequences are severe.
-
Host Discovery and Port Scan (Baseline):
First, we establish a baseline. A comprehensive port scan is essential to understand what's running on the target.
nmap -p- -sV -O-oN baseline_scan.txt -p-: Scans all 65535 TCP ports.-sV: Attempts to determine service version and type.-O: Enables OS detection.-oN: Saves the output to a file in normal format.
-
Running Vulnerability Scripts:
Now, we deploy the NSE scripts. Targeting the 'vuln' category is a good starting point. For broader coverage, you might include other categories like 'default' to catch common misconfigurations.
This command tells Nmap to perform a full port scan and then run all scripts categorized as 'vuln' against the discovered services.nmap -p- --script vuln-oN vuln_scan.txt -
Targeting Specific Vulnerabilities:
If you have a specific vulnerability in mind or want to test a particular service, you can specify the script. For example, to check for Heartbleed vulnerability (though deprecated, it exemplifies the concept):
Or, to check for common SMB vulnerabilities:nmap -p 443 --script ssl-heartbleed
The `smb-vuln-*` pattern will run all scripts starting with `smb-vuln`.nmap -p 445 --script smb-vuln-* -
Combining Scripts for Maximum Impact:
In a real-world scenario, you'd likely combine several script categories for a thorough assessment.
nmap -p- -sV -O --script vuln,default,discovery,safe-oN comprehensive_vuln_scan.txt vuln: Vulnerability detection scripts.default: Scripts that run by default with-sCor--script default.discovery: Scripts that discover information about hosts or services.safe: Scripts that are considered safe to run against most hosts, avoiding potential disruption.
-
Interpreting the Results:
The output file (e.g.,
vuln_scan.txt) will contain the results. Look for sections with "VULNERABLE" or specific CVE identifiers. Pay close attention to the script output, which often provides details about the vulnerability and potentially how to remediate it. This is where your analytical skills come into play. A raw finding isn't an actionable insight until you've assessed its true impact and context.
Remember, these scripts are tools. They require interpretation. A script might flag a potential issue, but it's your job to determine if it's a true vulnerability in your specific environment and what the actual risk is. This is where investing in advanced cybersecurity training, like the comprehensive courses offered on platforms such as HackerSploit Academy, becomes indispensable.
Veredicto del Ingeniero: ¿Vale la Pena Usar Nmap para Vulnerability Scanning?
Absolutely. Nmap, especially with NSE, is an indispensable tool in the arsenal of any security professional. It offers a level of detail and customization that many commercial tools struggle to match, often at a fraction of the cost. However, it's crucial to understand its limitations:
- False Positives/Negatives: NSE scripts are not perfect. They can produce false positives (flagging a vulnerability that doesn't exist) or false negatives (missing a vulnerability that does exist).
- Noise: Aggressive scanning with numerous NSE scripts can be noisy, potentially triggering Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) or alarming system administrators.
- Context is Key: Nmap identifies potential issues. Understanding the exploitability, impact, and context within your specific network is your responsibility.
For professional penetration testing and bug bounty hunting, Nmap is a staple. It's the first tool I reach for to baseline a target and begin identifying attack vectors. To truly master it, delve into resources that go beyond the basics. Consider courses that cover advanced Nmap techniques for penetration testing. The knowledge gained from experienced professionals can significantly shorten your learning curve and prevent costly mistakes.
"The network doesn't lie. It just speaks in a language of packets and protocols. Learn the language, and the secrets – the vulnerabilities – will be revealed."
Arsenal del Operador/Analista
- Core Tool: Nmap (Essential)
- Advanced Nmap Training: Nmap for Penetration Testing Course (Highly Recommended)
- Scripting Engine Documentation: NSE Documentation (Crucial for script understanding)
- Vulnerability Databases: CVE Details, NVD (For cross-referencing findings)
- Alternative/Complementary Scanners: Nessus, OpenVAS, Acunetix (Commercial/Open-source options for broader coverage or different focuses)
- Decentralized Content Platform: LBRY/Odysee (For alternative video access)
- Support & Community: HackerSploit (For community and resources)
Preguntas Frecuentes
-
Is Nmap a replacement for dedicated vulnerability scanners like Nessus or Qualys?
Nmap is an excellent tool for vulnerability scanning, especially with its NSE scripts. However, dedicated scanners often have larger, more frequently updated vulnerability databases and more advanced automated reporting features. Nmap is often used as a complementary tool or for initial reconnaissance. -
Can Nmap detect zero-day vulnerabilities?
Nmap's NSE scripts are based on known vulnerabilities. It cannot detect zero-day vulnerabilities unless a script has been specifically written and released for that particular zero-day. For zero-day detection, more advanced threat hunting and anomaly detection techniques are usually required. -
How can I ensure my Nmap scans don't disrupt services?
Use Nmap's timing templates (e.g.,-T4for aggressive but generally reasonably fast,-T3for normal) and specifically choose 'safe' NSE scripts that are designed to not cause instability. Always test in a controlled environment first. -
Where can I find more advanced Nmap NSE scripts?
The Nmap Scripting Engine documentation is the primary source. Additionally, repositories like GitHub often host custom or updated NSE scripts. Following security researchers and communities can also lead you to newly developed scripts.
El Contrato: Forge Your Own Network Reconnaissance Framework
The digital landscape is a battlefield. Nmap is your reconnaissance drone, your initial probe, your keen-eyed observer. But a true operator doesn't rely on a single tool; they build an integrated framework. Your challenge: Create a simple shell script that automates the process of running a baseline Nmap scan followed by a vulnerability scan using the 'vuln' category of NSE scripts. Save both outputs to timestamped files. This will teach you the fundamentals of scripting your operations and ensure you never miss a crucial scan when time is of the essence.
Now, go forth and map the shadows. But do it ethically, do it intelligently, and prepare for what you might find. The network is vast, and the vulnerabilities are many. Your vigilance is the first line of defense.

No comments:
Post a Comment