ÍNDICE DE LA ESTRATEGIA
- Introduction: The Alarming Ease of Phishing
- Deconstructing the Phishing Arsenal
- Mission Briefing: Deploying the Black Eye Phishing Tool
- Phase 1: Constructing a Malicious Phishing Website
- Phase 2: Executing the Phishing Email Campaign
- Beyond the Email: A Spectrum of Phishing Techniques
- CompTIA Security+ Resources: Your Official Intelligence Briefings
- The Engineer's Arsenal: Essential Tools & Intel
- Comparative Analysis: Black Eye vs. Advanced Frameworks
- The Engineer's Verdict on Phishing Defense
- Frequently Asked Questions
- About The Cha0smagick
- Mission Debrief & Next Steps
The digital landscape is a battleground, and understanding the enemy's tactics is paramount for survival. In this dossier, we dissect one of the most pervasive and deceptively simple threats: Phishing attacks. Far from being a mere nuisance, these well-crafted deceptions can compromise critical data, drain financial resources, and cripple organizational infrastructure. This is not just a theoretical overview; it’s a deep dive into the mechanics, a blueprint for understanding how these operations are launched, and critically, how to defend against them.
Advertencia Ética: La siguiente técnica debe ser utilizada únicamente en entornos controlados y con autorización explícita. Su uso malintencionado es ilegal y puede tener consecuencias legales graves.
This comprehensive guide serves as Episode 2 of our FREE CompTIA Security+ course, covering essential objectives for both the SY0-501 and SY0-601 certifications. We will explore the anatomy of phishing, its diverse variants, and demonstrate the deployment of a practical tool used in these operations. Your mission, should you choose to accept it, is to absorb this intelligence and fortify your defenses.
Deconstructing the Phishing Arsenal
Before we delve into practical deployment, it's crucial to understand the terminology and the specific vectors attackers employ. Phishing is an umbrella term for a variety of social engineering tactics designed to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that benefit the attacker. Here’s a breakdown of the common types:
- Phishing: The general term for fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information by disguising as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication.
- Smishing (SMS Phishing): Phishing attacks conducted via SMS text messages. These often contain links to malicious websites or urgent requests for information.
- Vishing (Voice Phishing): Phishing attacks perpetrated over the phone. Attackers impersonate legitimate organizations (banks, government agencies, tech support) to extract information or persuade victims to install malware.
- Spear Phishing: A highly targeted phishing attack. Attackers research their victims (individuals or organizations) to craft personalized and convincing messages, significantly increasing the success rate.
- Pharming: A sophisticated attack that redirects users from a legitimate website to a fraudulent one without their knowledge. This is often achieved by compromising DNS servers or a host's local system.
- Spam: Unsolicited bulk messages, typically commercial in nature, sent indiscriminately to a large number of recipients. While often an annoyance, spam can be a delivery mechanism for phishing attempts.
- SPIM (Spam over Internet Messaging): Similar to spam, but delivered via instant messaging platforms.
- Whaling: A type of spear phishing specifically targeting high-profile individuals within an organization, such as CEOs or senior executives, often with the goal of large-scale financial fraud or corporate espionage.
- Credential Harvesting: The specific act of collecting usernames and passwords, typically through fake login pages or forms presented during a phishing attack.
- Invoice Scams: A common phishing tactic where attackers send fraudulent invoices, often appearing to be from legitimate suppliers, to trick recipients into making payments or revealing financial details.
Mission Briefing: Deploying the Black Eye Phishing Tool
For this operational demonstration, we will utilize the Black Eye Phishing tool. This tool, while powerful, is a prime example of the technologies attackers can leverage. Understanding its functionality is key to recognizing and mitigating its impact.
Download Link: Black Eye Phishing Tool
This tool simplifies the process of creating convincing phishing pages. The following steps outline its deployment and use. Remember, this is for educational purposes to understand the attack vector.
Phase 1: Constructing a Malicious Phishing Website
- Installation: Ensure you have the necessary prerequisites for Black Eye installed on your system. This typically involves Python and potentially other libraries. Follow the installation guide provided with the tool.
- Launching the Tool: Execute the Black Eye script from your terminal.
- Template Selection: Black Eye offers various templates that mimic legitimate websites (e.g., login pages for popular services like Google, Facebook, or banking portals). Choose a template that aligns with your intended target.
- Configuration: Configure the tool to host the phishing page. This might involve setting up a local web server or, for more advanced operations, using a compromised or purchased domain with hosting. The tool will guide you through specifying the target URL for credential redirection. For instance, if you choose a Google login template, you will configure it to send harvested credentials to a specific endpoint you control.
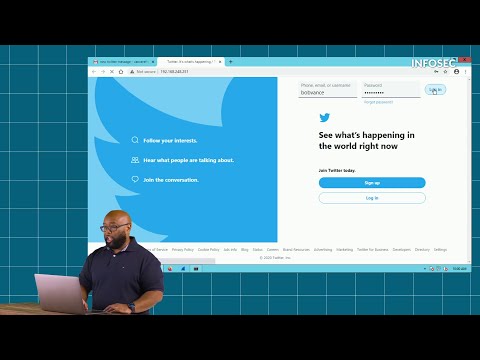
- Website Generation: Once configured, Black Eye generates the phishing website. This page will look identical to the legitimate site, designed to fool users into entering their credentials.
Phase 2: Executing the Phishing Email Campaign
A convincing website is only half the battle. The other half is luring your target to it. Attackers often use email to distribute phishing links.
- Crafting the Malicious Email: Write an email that appears to be from a legitimate source. This could be a fake notification from a shipping company, a password reset request from a service provider, or an urgent security alert. The email should create a sense of urgency or curiosity, prompting the recipient to click the provided link.
- Embedding the Phishing Link: Insert the URL of your Black Eye-generated phishing page into the email. This link can be disguised using URL shorteners or by embedding it within seemingly innocuous text or buttons.
- Sending the Campaign: Use an email client or a dedicated bulk email sending tool to send the phishing emails to your targets. For realistic simulations, consider using tools that allow for email spoofing (though this requires advanced knowledge and ethical considerations).
- Credential Harvesting: When a victim clicks the link and enters their credentials on the fake login page, Black Eye captures this information. The tool will typically log these credentials to a file for the attacker to retrieve.
Beyond the Email: A Spectrum of Phishing Techniques
While email phishing and credential harvesting are common, attackers employ a variety of methods:
- Smishing: Attackers send SMS messages with malicious links, often impersonating banks or delivery services. The urgency is conveyed through short, direct messages.
- Vishing: Phone calls where attackers impersonate IT support or government officials. They might ask for remote access to your computer or demand payment for fake services or fines.
- Spear Phishing & Whaling: These highly personalized attacks require significant reconnaissance. Attackers might leverage information from social media, company websites, or previous breaches to craft incredibly believable messages tailored to the individual or executive.
- Pharming: This attack bypasses the need for a convincing email. By manipulating DNS records or hosts files, any attempt to visit a legitimate website can be redirected, making it incredibly difficult to detect.
CompTIA Security+ Resources: Your Official Intelligence Briefings
To truly master cybersecurity, foundational knowledge is essential. The CompTIA Security+ certification provides a robust framework for understanding these threats. Here are key resources to deepen your understanding:
- Official CompTIA Study Guide: Purchase the official guide for a structured learning path.
- CompTIA eLearning: Explore interactive learning modules and practice exams from CompTIA eLearning.
- Collaborative Course: This episode is part of a FREE Security+ course, created in collaboration with industry experts David Bombal and the late, great Jeremy Cioara (Keeping IT Simple).
- Security+ Playlist: Access all episodes in the series here: Security+ Playlist.
The Engineer's Arsenal: Essential Tools & Intel
As an operative in the digital realm, your toolkit is as vital as your intellect. Beyond specific phishing tools, consider these resources:
- CEH Study Tools: For those aiming for Certified Ethical Hacker certification, explore comprehensive resources like ITProTV for video training and labs, and essential books available on Amazon or via a 10-day FREE TRIAL on O'Reilly.
- Programming for Automation: Skills in languages like Python are invaluable. Consider Codecademy's Python courses to build your own security tools or automate defense mechanisms.
- Network Gear & Recommendations: For building secure and robust networks, explore recommended gear: My Network Gear.
- General Recommendations: Check out my curated list of tech and tools on Amazon.
- Raspberry Pi: A versatile tool for various tech projects, including security labs. Buy a Raspberry Pi here.
Comparative Analysis: Black Eye vs. Advanced Frameworks
While Black Eye is a straightforward tool for demonstrating phishing principles, the professional threat landscape involves more sophisticated frameworks. Tools like SET (Social-Engineer Toolkit) offer a wider array of attack vectors, including more advanced credential harvesting techniques, website cloning, and payload delivery. SET is highly configurable and integrates with various social engineering methodologies. For true offensive operations, frameworks like Empire or commercial pentesting suites provide more robust capabilities for post-exploitation, lateral movement, and persistence. However, for educational purposes, Black Eye effectively illustrates the core mechanism of phishing page creation and credential interception.
The Engineer's Verdict on Phishing Defense
Phishing attacks prey on human psychology – trust, fear, and urgency. While technical defenses like email filters and web security gateways are crucial, they are not infallible. The most potent defense lies in user education and vigilance. Every individual interacting with digital systems must be trained to scrutinize communications, verify sources, and question unsolicited requests for sensitive information. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a non-negotiable step, as it provides a critical second layer of security even if credentials are compromised.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary goal of a phishing attack?
The primary goal is to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card details, or other personally identifiable information, or to compromise their systems by installing malware.
How can I protect myself from phishing?
Be skeptical of unsolicited communications, verify the sender's identity, avoid clicking suspicious links or downloading attachments, use strong, unique passwords, and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible. Regularly update your software and use reputable security solutions.
Is using a tool like Black Eye illegal?
Using tools like Black Eye to attack systems or individuals without explicit, written authorization is highly illegal and carries severe penalties. Their purpose is for educational and ethical security testing in controlled environments only.
What is the difference between phishing and spear phishing?
Phishing is a broad, untargeted attack, while spear phishing is a highly targeted attack customized for a specific individual or organization, making it much more convincing and dangerous.
How do pharming attacks work?
Pharming attacks redirect users from legitimate websites to malicious ones by corrupting the Domain Name System (DNS) resolution process or by modifying the host files on a user's computer. This means even typing the correct URL can lead to a fake site.
About The Cha0smagick
I am The Cha0smagick, an engineer and ethical hacker with a passion for demystifying complex technological landscapes. My mission is to translate intricate concepts into actionable intelligence and practical blueprints. Sectemple serves as a repository of dossiers, providing the elite operative with the knowledge needed to navigate and dominate the digital frontier. I believe in empowering individuals through knowledge, fostering a proactive approach to cybersecurity and technological mastery.
Mission Debrief & Next Steps
You have now been briefed on the mechanics of phishing attacks and have seen a practical demonstration of how one such operation can be initiated. Understanding these attack vectors is the first line of defense. The ease with which these operations can be launched is indeed alarming, but knowledge is your most potent weapon.
"The greatest security for any organization is a well-informed and vigilant workforce."
The digital world is constantly evolving, and so must your strategies. Continuous learning and adaptation are not optional; they are survival imperatives. Remember, for every exploit, there is a countermeasure. For every attack, there is a defense.
Your Mission: Execute, Share, and Debate
If this dossier has equipped you with critical intelligence or saved you valuable operational time, your next directive is clear: share this knowledge. An informed network is a stronger network.
- Share the Blueprint: Transmit this knowledge to your network. Equip your colleagues and peers with this vital intel.
- Engage in Debriefing: Did you find this analysis insightful? Do you have questions, or perhaps real-world scenarios to discuss? Drop your thoughts in the comments below. Each debriefing session sharpens our collective understanding.
- Demand Future Dossiers: What threat vectors or technologies should we dissect next? Your input shapes our intelligence priorities. Let us know what you need to master.
Now, go forth and fortify your defenses. The digital frontier awaits.