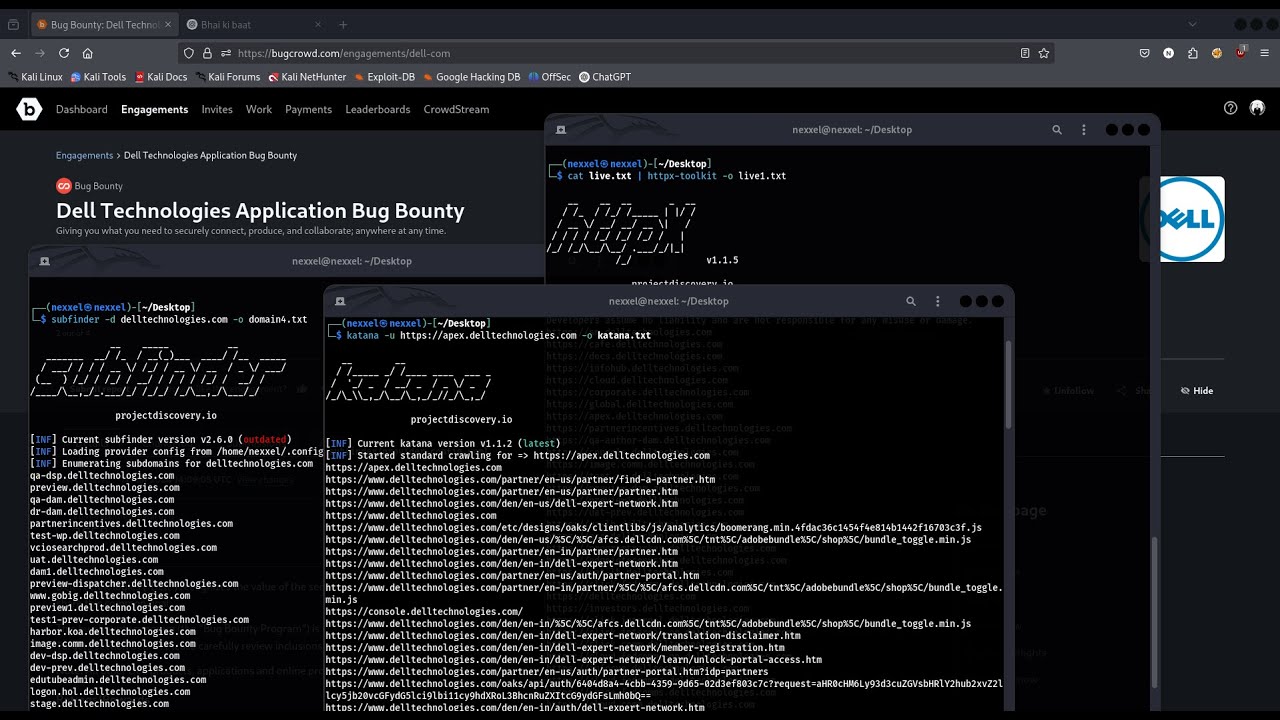
The digital frontier is a battlefield, and in the realm of cybersecurity, intelligence is your most potent weapon. Bug bounty hunting on platforms like Bugcrowd is not merely about finding vulnerabilities; it's a meticulous process of reconnaissance, understanding the target's digital footprint, and systematically identifying potential weaknesses. This dossier, "Live Bug Bounty Hunting on Bugcrowd: Live Recon | Part 1," is your foundational training in real-time intelligence gathering.
Advertencia Ética: La siguiente técnica debe ser utilizada únicamente en entornos controlados y con autorización explícita. Su uso malintencionado es ilegal y puede tener consecuencias legales graves.
ESTRATEGIA INDEX
- Manual Subdomain Discovery: The Foundation
- Automated Subdomain Enumeration: Scaling Your Recon
- Subdomain Brute-Forcing: Uncovering Hidden Assets
- Live Domain Verification: Ensuring Reachability
- Screenshotting for Visual Reconnaissance
- Deep Reconnaissance Tools: Unveiling Hidden Depths
- URL and JavaScript Analysis: Mapping the Attack Surface
- Path and Parameter Discovery: Identifying Entry Points
- Subdomain Takeover Vulnerability Detection
- Port Scanning for Open Services
- Leveraging Google Dorking for Intelligence
- Introduction to Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Discovery
- The Engineer's Arsenal
- Engineer's Verdict
- Frequently Asked Questions
- About the Author
Manual Subdomain Discovery: The Foundation
Before automating, understanding the manual methods for subdomain discovery is crucial. This forms the bedrock of your reconnaissance operations. By leveraging specialized search engines and databases, you can begin to map out the attack surface.
- Certificate Transparency Logs (crt.sh): A primary source for discovering subdomains associated with SSL/TLS certificates. By querying `crt.sh`, you can find historical and active certificates, revealing associated domains.
- Query Example: `https://crt.sh/?q=%.example.com` (Replace `example.com` with your target domain)
- VirusTotal: While primarily an antivirus engine, VirusTotal's domain and IP history can reveal associated subdomains and their connections.
- Access: VirusTotal URL Analysis
- Chaos Project (ProjectDiscovery): An open-source project that provides a vast network of internet-wide scan data, including subdomains.
- Access: Chaos Project
Automated Subdomain Enumeration: Scaling Your Recon
Manual methods are effective but time-consuming. Automation is key to scaling your operations and covering larger attack surfaces efficiently. Several powerful tools are available:
- Subfinder (ProjectDiscovery): A fast and reliable subdomain enumerator that uses various sources.
- GitHub: ProjectDiscovery/subfinder
- Assetfinder: A simple yet effective tool for finding subdomains.
- GitHub: tomnomnom/assetfinder
- Sublist3r: A popular Python tool that enumerates subdomains using multiple search engines.
- Amass: A comprehensive brute-force, enum, and analysis tool that performs network mapping.
- GitHub: owasp-amass/amass
Subdomain Brute-Forcing: Uncovering Hidden Assets
Beyond passive enumeration, brute-forcing involves using wordlists to guess potential subdomains that might not be registered or publicly discoverable through other means. This requires a robust wordlist and efficient brute-forcing tools.
- FFuF (Fast Web Scanner): A highly performant web fuzzer that can be used for subdomain brute-forcing.
- GitHub: ffuf/ffuf
- Gobuster: A versatile directory and brute-force attacker.
- DirBuster: A Java-based web analysis tool.
- Amass (again): Amass also includes sophisticated brute-forcing capabilities.
- Wordlists: High-quality wordlists are paramount.
- Seclists: A comprehensive collection of security-related wordlists.
- n0kovo's Wordlists: A curated collection for specific tasks.
- GitHub: n0kovo_subd...
Live Domain Verification: Ensuring Reachability
After enumerating subdomains, it's vital to determine which of them are actually live and responding. This step filters out dead entries and focuses your efforts.
- HTTPX (ProjectDiscovery): A fast and multifunctional HTTP client that allows you to run multiple modules on your targets. It can check for live domains, status codes, title, and more.
- GitHub: projectdiscovery/httpx
Screenshotting for Visual Reconnaissance
Visual inspection can often reveal vulnerabilities or unique application characteristics that automated scans might miss. Taking screenshots of all live subdomains provides a quick overview.
- GoWitness: Tool designed to take screenshots of websites across numerous hosts.
- GitHub: sensepost/gowitness
Deep Deep Reconnaissance Tools: Unveiling Hidden Depths
For a more thorough understanding of the target's infrastructure, specialized tools can uncover a wealth of information, including hidden files, directories, and underlying technologies.
- OneForAll: A powerful subdomain enumeration tool that integrates various methods for a comprehensive scan.
- GitHub: shmilylty/OneForAll
URL and JavaScript Analysis: Mapping the Attack Surface
Understanding the structure of a web application, including all accessible URLs and the JavaScript files it utilizes, is critical for identifying potential entry points and logic flaws.
- Waybackurls: Extracts URLs from the Wayback Machine.
- Katana: A fast web reconnaissance framework for crawling, scraping, and analyzing assets.
- GitHub: projectdiscovery/katana
- LinkFinder: A Python tool for extracting endpoints from JavaScript files.
- GitHub: GerbenJavado/LinkF...
- Subjs: Extracts JavaScript files from subdomains.
- GitHub: lc/subjs
- Katana (with JavaScript context): Can be used with flags like `-jc` to extract JavaScript data.
Path and Parameter Discovery: Identifying Entry Points
Once you have a list of URLs, the next step is to discover hidden paths and parameters that might be vulnerable to various attacks.
- Dirsearch: A fast web directory scanner.
- FFuF: As mentioned before, FFuF is highly effective for discovering directories and files.
- GitHub: ffuf/ffuf
- Arjun: An HTTP parameter discovery suite that helps in finding hidden parameters.
- GitHub: s0md3v/Arjun
Subdomain Takeover Vulnerability Detection
Misconfigured subdomains can sometimes be hijacked and pointed to attacker-controlled resources. Tools can help identify potential takeover candidates.
- Subzy: An automated tool for quick subdomain takeover scanning.
- GitHub: PentestPad/subzy
- SocialHunter: While focused on social media, its principles can be adapted for identifying misconfigurations.
- GitHub: utkusen/socialhunter
Port Scanning for Open Services
Identifying open ports and the services running on them is a fundamental aspect of network reconnaissance. It helps in understanding the attack surface exposed by the target's infrastructure.
- Nmap: The de facto standard for port scanning and network discovery.
- Command Example: `nmap -p- -T4 -sC -sV
`
- Command Example: `nmap -p- -T4 -sC -sV
Leveraging Google Dorking for Intelligence
Search engines like Google can be powerful reconnaissance tools when used with advanced search operators (dorks). These can uncover sensitive information, configuration files, and vulnerable endpoints.
- Google Dorking Resources: Numerous guides and tools can assist in crafting effective Google Dorks for bug bounty hunting.
- Guide Example: Bug Bounty Google Dorking Guide
Introduction to Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Discovery
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is a common vulnerability that allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users. Basic detection often involves identifying parameters that might be vulnerable to script injection.
- XSS Discovery Tools: Various tools and techniques can assist in finding XSS vulnerabilities.
- Tool Example: XSS Detection Tool
The Engineer's Arsenal
To excel in the field of bug bounty hunting, a robust toolkit is essential. Beyond the specific tools mentioned, consider these foundational resources:
- Books: "The Web Application Hacker's Handbook," "Penetration Testing: A Hands-On Introduction to Hacking."
- Platforms: Bugcrowd, HackerOne, Intigriti.
- Learning Resources: PortSwigger Web Security Academy, Cybrary, TryHackMe, Hack The Box.
- Version Control: Git and GitHub for managing your scripts and findings.
Engineer's Verdict
This first part of our live recon mission on Bugcrowd lays the groundwork. Mastering subdomain enumeration, verification, and initial reconnaissance is non-negotiable. The tools outlined here are not merely commands; they are extensions of your analytical capabilities. The real skill lies in understanding how to chain these tools together, interpret their output, and apply critical thinking to uncover vulnerabilities. This is the essence of efficient and effective bug bounty hunting.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the most critical first step in bug bounty hunting?
The most critical first step is comprehensive reconnaissance, starting with understanding the target's scope and performing thorough subdomain enumeration.
-
How can I ensure I'm performing bug bounty hunting legally?
Always adhere to the rules of engagement set by the bug bounty program. Never test systems without explicit permission. Focus on disclosing vulnerabilities through the official channels provided.
-
Are these tools free to use?
Most of the tools mentioned are open-source and free to use. Some platforms or advanced services might have associated costs.
-
What should I do after finding a potential vulnerability?
Document your findings meticulously, including steps to reproduce the vulnerability, its impact, and a suggested remediation. Submit your report through the designated platform channel (e.g., Bugcrowd).
About the Author
The Cha0smagick is a seasoned cybersecurity operative and polymath engineer, specializing in reverse engineering, advanced persistent threat analysis, and offensive/defensive security architecture. With years spent navigating the deepest trenches of the digital realm, The Cha0smagick transforms complex technical challenges into actionable intelligence and robust solutions. This blog, Sectemple, serves as a repository of 'dossiers' for aspiring digital operatives, offering unparalleled insights and practical training.
Your Mission: Debrief and Diversify
This dossier has equipped you with the initial phase of live recon on Bugcrowd. The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and so must your skillset. A crucial element of long-term success, both in cybersecurity and in personal finance, is diversification. For managing digital assets and exploring financial opportunities, consider opening an account on Binance to explore the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Now, operatives, it's time for your debriefing. Share your initial thoughts, any tools you find particularly effective, or challenges you've encountered in the comments below. Your intelligence is valuable.
Debriefing of the Mission
What are your primary takeaways from this initial reconnaissance phase? Which tool is now at the top of your list to master? Engage in the discussion below, and let's refine our operational tactics together.
Bug Bounty, Cybersecurity, Ethical Hacking, Reconnaissance, Bugcrowd, Penetration Testing, Tools, Live Recon
No comments:
Post a Comment