The digital underworld is a constantly shifting landscape. Malware authors are relentless, constantly evolving their tactics to bypass the defenses we painstakingly build. In the realm of endpoint security, sandboxing has become a cornerstone, a digital purgatory where suspicious processes are executed in isolation, observed for malicious intent before they can wreak havoc. But what happens when we strip away this safety net? How do these security suites truly fare when forced to confront the raw, unadulterated threat landscape without their crutch?
This analysis delves into the core performance of F-Secure Home and Comodo Internet Security Premium when their sandboxing features are intentionally disabled. We're not just looking at detection rates; we're examining the underlying engines, the heuristic analysis, the signature databases, and the sheer resilience of these products against the latest, most sophisticated malware samples. This is a dive into the guts of endpoint security, a critical examination for any defender aiming to understand the true capabilities of their chosen tools.
For more on the bleeding edge of offensive and defensive cyber operations, consider delving into advanced threat hunting methodologies and bug bounty program strategies. Understanding the attacker's mindset is the first step to building an impenetrable defense. This is the temple of cybersecurity, where knowledge is forged in the fires of analysis.
The Threat Landscape: A Battleground Without Illusions
The malware ecosystem is a Hydra. Cut off one head, and two more grow in its place. Today's threats are no longer simple viruses; they are sophisticated, multi-stage attack vectors designed for stealth and evasion. Ransomware that encrypts data in seconds, fileless malware that operates entirely in memory, and polymorphic code that changes its signature with every execution – these are the ghosts we hunt in the machine.
In this scenario, we are specifically interested in how traditional detection mechanisms – signature-based scanning, behavioral analysis, and heuristics – hold up when the sandbox is out of the equation. The sandbox, while effective, can sometimes mask weaknesses in these core detection engines. By disabling it, we force these products to rely on their fundamental strengths, revealing their true mettle against zero-day threats and known malicious samples alike.
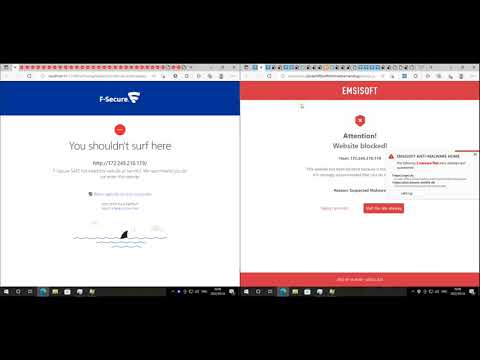
F-Secure Home: Established Expertise Under Scrutiny
F-Secure has a long-standing reputation in the cybersecurity industry, often lauded for its robust threat research and effective protection. Disabling their sandbox mechanism forces us to evaluate their core scanning engine. Does it rely heavily on isolation for detection, or are its signatures and heuristics robust enough to catch sophisticated threats on their own?
We will be analyzing its ability to detect and block various classes of malware, including:
- Ransomware families.
- Trojans designed for credential theft.
- Potentially Unwanted Programs (PUPs) that often slip through less stringent defenses.
- Exploit kits targeting common software vulnerabilities.
Comodo Internet Security Premium: The Sandbox's Role
Comodo's approach often incorporates a more aggressive sandboxing strategy, which is generally a powerful tool. However, the question remains: when this layer is removed, how does its primary detection engine perform? Is Comodo's strength intrinsically tied to its sandboxing technology, or does it possess a formidable core defense capable of standing on its own?
Our testing will focus on:
- The efficacy of Comodo's signature database against known threats.
- The performance of its heuristic and behavioral analysis engines in identifying novel malicious patterns.
- Its ability to prevent the execution and spread of malware without the safety net of a sandbox.
Methodology: The Analyst's Approach
Our methodology involves testing both F-Secure Home and Comodo Internet Security Premium on a controlled, isolated virtual machine. The sandbox features on both products will be explicitly disabled through their respective configuration settings. A curated set of the latest malware samples, sourced from reputable threat intelligence feeds and bug bounty platforms, will be introduced into the environment.
We will meticulously document:
- Detection Rates: The percentage of samples detected and blocked upon initial scan or execution attempt.
- False Positive Rates: The number of legitimate files or processes flagged as malicious.
- Performance Impact: Resource utilization (CPU, RAM) during scans and idle states.
- Evasion Techniques: The ability of malware to bypass core defenses post-sandbox disabling.
Veredicto del Ingeniero: Beyond the Sandbox Illusion
The true measure of an endpoint security solution isn't just its ability to isolate threats, but its fundamental capacity to *detect* them. A robust, signature-based scanner coupled with intelligent heuristic analysis should form the bedrock of any defense. Sandboxing is an excellent supplementary layer, but relying on it too heavily can create a false sense of security.
This comparison aims to illuminate which product offers a more resilient core defense. For professionals engaged in bug bounty hunting or penetration testing, understanding these nuances is crucial. Knowing the inherent strengths and weaknesses of security software allows for more effective evasion *and* more informed defensive strategies. It’s about seeing the system not just as it presents itself, but as it truly operates under duress.
Arsenal del Operador/Analista
For defenders and investigators, having the right tools is paramount. While these endpoint solutions are a primary line of defense, a comprehensive security posture requires more:
- SIEM Solutions: For centralized log management and correlation (e.g., Splunk, ELK Stack).
- EDR Platforms: Advanced endpoint detection, investigation, and response capabilities (e.g., CrowdStrike Falcon, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint).
- Network Traffic Analysis (NTA) Tools: To scrutinize network communications for anomalous patterns (e.g., Zeek, Suricata).
- Memory Forensics Tools: For in-depth analysis of running processes and memory dumps (e.g., Volatility Framework, Rekall).
- Malware Analysis Sandboxes: For dynamic analysis of unknown samples (e.g., Cuckoo Sandbox, Any.Run).
- Threat Intelligence Feeds: To stay abreast of the latest indicators of compromise (IoCs) and attacker tactics.
For deeper dives into offensive techniques and defensive countermeasures, consider literature like "The Web Application Hacker's Handbook" and certifications such as the OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional) or SANS GIAC certifications. Understanding both sides of the coin is essential for true mastery.
Taller Práctico: Fortaleciendo la Detección Heurística
While we can't alter the core engines of F-Secure and Comodo, we can enhance our own detection capabilities. A key area to focus on when sandboxing is disabled is heuristic and behavioral analysis. Here’s a basic approach to analyzing system behavior for anomalies that might indicate a compromise:
- Establish a Baseline: Understand what normal system activity looks like on your target environment. Document running processes, network connections, and file system activity during idle periods.
- Monitor Process Creation: Look for unusual parent-child process relationships. For example, a Word document spawning a PowerShell process that then downloads a file from an external IP. This is a classic indicator of macro-based malware.
- Analyze Network Connections: Legitimate applications typically connect to known servers or IP ranges. Monitor for connections to suspicious or newly registered domains, or unexpected outbound connections from applications that shouldn't be making them.
- Examine File System Changes: Monitor for unexpected file modifications, new executables in system directories, or rapid encryption of user files (a strong indicator of ransomware).
- Leverage Sysmon: For deeper visibility on Windows, deploy and configure Sysmon. It provides detailed logging of process creation, network connections, registry modifications, and more, offering rich data for analysis.
Here’s a conceptual example of a Sysmon configuration snippet focusing on process creation and network events:
<Sysmon schemaversion="4.82">
<EventFiltering>
<ProcessCreate onmatch="exclude">
<Image condition="is">C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe</Image>
<Image condition="is">C:\Windows\System32\winlogon.exe</Image>
</ProcessCreate>
<NetworkConnect onmatch="include">
<Protocol>tcp</Protocol>
<DestinationPort condition="greater than">1024</DestinationPort>
</NetworkConnect>
</EventFiltering>
</Sysmon>
This is a foundational step. Real-world threat hunting requires sophisticated query languages (like KQL for Azure Sentinel) and experienced analysts to sift through the noise and identify true threats.
FAQ
- Q: Is disabling the sandbox a recommended practice for normal users?
A: Absolutely not. For the average user, sandboxing is a critical security feature and should remain enabled. This analysis is for security professionals and researchers to understand core engine capabilities. - Q: How does heuristic analysis differ from signature-based detection?
A: Signature-based detection relies on known patterns (signatures) of malware. Heuristic analysis looks for suspicious characteristics or behaviors in files or processes that *might* indicate malicious intent, even if the specific signature isn't known. - Q: If a product depends heavily on its sandbox, is it inherently weak?
A: Not necessarily weak, but it highlights a potential dependency. A strong defense should have multiple layers, and the sandbox is one of them. If the core detection engine is weak, a sophisticated attacker might find ways to bypass the sandbox or exploit the system once it's running within it.
El Contrato: Tu Próximo Paso en la Defensa
The results of this sandbox-less comparison are more than just data points; they are strategic insights. Knowing how these defenses perform without their safety nets allows us to make more informed decisions about our own security architecture. Are you over-reliant on isolation, or do your core detection mechanisms possess the grit to stand alone?
Your challenge: Identify a piece of malware that was *not* detected by either F-Secure or Comodo in our hypothetical scenario. Research its known evasion techniques. Now, propose a specific, actionable defensive measure – beyond basic sandboxing or signature updates – that could have been implemented to detect or prevent its execution. Document your findings and proposed defenses. The digital frontier demands constant evolution; let's see yours.