The hum of the server room was a low thrum, a constant reminder of the digital fortresses we build. But even the strongest walls have cracks. In the shadowy corners of the network, whispers of malicious code and unseen intruders persist. Today, we're not just talking about defense; we're talking about the hunt. We're peeling back the layers to expose the enemy, using a tool that cuts through the noise: Aurora Light and its sharp Sigma rules. Forget the illusion of security; let's talk about tangible detection.
Decoding the Threat Landscape
In this never-ending digital war, the battlefield is your endpoint. Hackers aren't just brute-forcing their way in anymore; they're sophisticated. They plant seeds of malware, exploit zero-days, and hide in plain sight. Cybersecurity isn't about building impenetrable castles; it's about having an elite recon team on constant watch. It's about knowing when the perimeter is breached, not hoping it won't be. This is where the art of detection meets the science of threat hunting.
Enter Aurora Light: Your Digital Bloodhound
Aurora Light isn't just another security tool; it's your silent sentinel, your digital bloodhound. This platform is engineered for Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), designed to sniff out the faintest traces of malicious activity. Think of it as a highly trained operative, meticulously scanning logs, processes, and network traffic for anomalies that scream "intruder." It’s built to see the shadows others miss.
Sigma Rules: The Language of Suspicion
The real muscle behind Aurora Light’s detection capabilities lies in its Sigma rules. These aren't just generic signatures; they're carefully crafted logic statements designed to flag suspicious behaviors, not just known malware. Whether it's an unusual process spawning, a suspicious network connection, or a specific registry modification, Sigma rules translate these digital footprints into actionable alerts. They are the grammar of our threat hunting language, allowing us to articulate what "looks wrong" in a way a machine can understand.
Tailoring Your Defense: Customizing the Arsenal
The beauty of a seasoned operative is adaptability. Aurora Light mirrors this with its robust customization options for Sigma rules. Generic rules are a starting point, but your environment is unique. You need to tune these rules, create your own, and refine them to eliminate false positives while amplifying the real threats. This isn't about blindly following playbooks; it's about crafting a personalized intelligence apparatus that fits your specific operational needs.
The Free Tier: Access for the Vigilant
Not everyone operates with an unlimited budget. The digital realm is rife with threats, and defense shouldn't be exclusive. Aurora Light offers a free version, democratizing advanced threat detection. This isn't a watered-down imitation; it provides essential capabilities for individuals and small teams to start building a more resilient security posture. It's your entry ticket to effective threat hunting without a king's ransom.
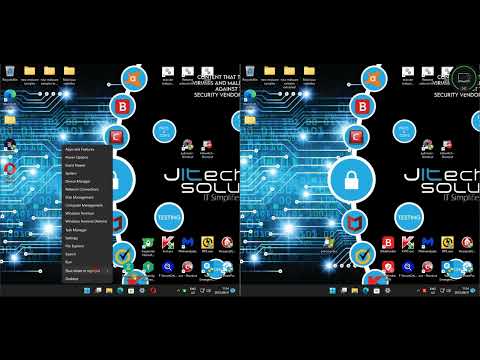
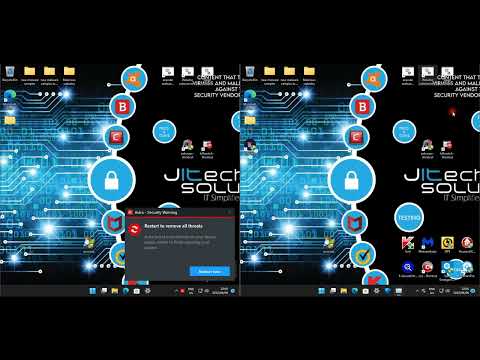
Operationalizing Detection: A Hands-On Approach
Theory is one thing, but the real test is in the field. Now, let's get our hands dirty. We'll walk through configuring Aurora Light and demonstrating how its Sigma rules can be leveraged for tangible threat detection. This is where abstract concepts become concrete actions, turning you from a passive observer into an active defender.
System Configuration: Setting the Stage
- Download and Installation: Acquire the Aurora Light client and follow the installation guide for your target operating system. Ensure you understand the system requirements and any dependencies.
- Agent Deployment: For server environments or multiple endpoints, plan your deployment strategy. This might involve remote installation scripts or manual setup.
- Initial Configuration: Access the Aurora Light console. Configure basic settings such as log forwarding, alert thresholds, and integration points with your existing security infrastructure.
- Network Considerations: Ensure necessary firewall rules are in place to allow communication between the Aurora Light agent and its central management console.
Exploring the Sigma Rulebook
- Rule Repository: Navigate to the Sigma rule management section within Aurora Light. Familiarize yourself with the pre-loaded rule sets.
- Rule Interpretation: Select a rule (e.g., detecting suspicious PowerShell execution). Analyze its conditions: the log sources it monitors, the specific fields it checks, and the logic operators used (`and`, `or`, `not`).
- Behavioral Analysis: Understand *why* a rule triggers. For instance, a rule looking for `powershell.exe` with encoded commands indicates an attacker attempting to obfuscate their payload.
- Tuning for Accuracy: Monitor alerts generated by the rules. If a rule is too noisy with false positives, adjust its parameters. This might involve adding exclusion lists or refining the detection logic.
- Custom Rule Creation: If you identify a specific threat vector unique to your environment, craft a custom Sigma rule. This requires a deep understanding of your logs and attacker techniques.
The Unsung Heroes: Supporting Security Analysts
Behind every effective detection system are skilled analysts. They are the ones who interpret the alerts, hunt for deeper compromises, and patch the vulnerabilities the attackers exploit. They work tirelessly, often in high-pressure situations, to keep our digital world secure. Their role is critical, and their expertise is what turns raw data into actionable intelligence.
Recognizing the Guardians
It's imperative that we acknowledge and support these digital guardians. Their dedication is often unseen, their battles fought in the quiet hours when most are asleep. Promoting awareness about their crucial work and ensuring they have the tools and recognition they deserve is not just good practice; it's essential for a robust cybersecurity ecosystem. Let's give them the respect they’ve earned.
Veredicto del Ingeniero: ¿Vale la pena adoptarlo?
Aurora Light, especially when leveraging Sigma rules, offers a potent and accessible solution for enhancing endpoint detection. The free version makes it a no-brainer for users looking to move beyond basic antivirus. The power comes from understanding and tuning Sigma rules, which requires a commitment to learning. It's not a magic bullet, but if you're willing to invest the time in customization and analysis, it transforms from a detection tool into an offensive counter-intelligence platform. For budget-conscious teams and security enthusiasts, it's an invaluable addition to the arsenal. For enterprises, it's a strong contender for augmenting existing EDR solutions or filling gaps in monitoring.
Arsenal del Operador/Analista
- Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR): Aurora Light (Free Tier), Sysmon, Velociraptor
- Log Analysis & SIEM: ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), Splunk, Graylog
- Threat Hunting Frameworks: Sigma Rule Repository, MITRE ATT&CK Framework
- Network Analysis: Wireshark, Zeek (Bro)
- Books: "The Art of Memory Analysis" by Michael Ligh, "Practical Threat Hunting and Incident Response" by Kyle Kauwema
- Certifications: GIAC Certified Incident Handler (GCIH), Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
Preguntas Frecuentes
- ¿Qué tan efectivo es Aurora Light para detectar malware desconocido (zero-day)?
- Aurora Light's effectiveness against zero-days relies heavily on the sophistication of its behavioral detection rules (Sigma). While it may not have a specific signature, anomalous behavior patterns flagged by well-crafted Sigma rules can still detect novel threats.
- Can I use Aurora Light on macOS or Linux?
- Check the official Aurora Light documentation for supported operating systems. The core Sigma rule engine is cross-platform, but agent support varies.
- How often should Sigma rules be updated?
- Sigma rules should be reviewed and updated regularly, ideally daily or weekly, depending on the threat landscape and your environment's specific risks. New threats emerge constantly, requiring updated detection logic.
El Contrato: Forging Your Detection Strategy
Your mission, should you choose to accept it, is to implement one custom Sigma rule within Aurora Light that targets a specific threat observed in your network or a common attack technique. Document the rule, the threat it aims to detect, and the expected alert output. Share your findings and the challenges encountered in the comments below. Prove you can adapt the theory into practice and strengthen the collective defense.