The digital airwaves hum with data, a constant stream of packets traversing the ether. But within this seemingly invisible flow, critical vulnerabilities lie dormant, waiting for the opportune moment to be exploited. Today, we dissect a common vector: the compromise of WPA and WPA2 Wi-Fi connections. Forget the romanticized notions of lone hackers in darkened rooms; this is about methodical analysis and understanding the silent weaknesses that plague our wireless perimeters. We're not just looking at how keys are broken; we're examining the anatomy of the attack to engineer stronger defenses.
The landscape of wireless security has evolved, yet many organizations still rely on protocols that, while once cutting-edge, now present inherent risks. WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) and its successor, WPA2, were designed to fortify wireless networks against unauthorized access. However, the strength of these protocols hinges critically on their implementation and, more importantly, the complexity and secrecy of the pre-shared key (PSK) or the robust nature of enterprise authentication. When these pillars crumble, the network becomes an open book.
Understanding the WPA/WPA2 Attack Vector
At its core, WPA/WPA2 encryption relies on a shared secret – the pre-shared key (PSK) – to authenticate devices and encrypt traffic. Attacks typically target the process of establishing this shared secret. The primary methods exploit either weak PSKs or the network's behavior when clients connect.
The Weakness: The Human Element in Key Management
The most significant vulnerability in WPA/WPA2-PSK is universally the user. Humans, by nature, favor convenience and memorability over cryptographic strength. This leads to the widespread use of:
- Commonly Used Passwords: "password123", "12345678", SSIDs themselves, or easily guessable phrases.
- Dictionary Words: Single words or simple combinations found in standard dictionaries.
- Personal Information: Names, birthdays, addresses, or pet names.
These predictable choices transform what should be a robust encryption barrier into a fragile facade, susceptible to brute-force or dictionary-based attacks.
Dictionary Files and Brute-Force Attacks
A dictionary file is simply a text file containing a list of potential passwords. Attackers leverage this by feeding these lists into specialized software that attempts to authenticate against the target network. If the network's PSK is present in the dictionary file, the authentication succeeds.
Brute-force attacks go a step further. Instead of relying on pre-compiled lists, they systematically generate every possible combination of characters, numbers, and symbols until a match is found. While computationally intensive, advancements in hardware and software make this a viable, albeit time-consuming, strategy for shorter or less complex keys.
The Technical Execution: Analyzing the Attack Tools
To understand how to defend against these attacks, one must understand the tools of engagement employed by threat actors. For WPA/WPA2 cracking, the suite of choice often includes tools like Aircrack-ng.
Setting the Stage: The Demolition Environment
Before any meaningful analysis can occur, the attacker needs to capture the necessary data. This involves:
- Compatible Wireless Adapter: A network interface card (NIC) capable of operating in monitor mode is essential. This mode allows the NIC to capture all wireless traffic within range, not just traffic addressed to it.
- Specific Software: Tools like
Airodump-ng(part of the Aircrack-ng suite) are used to sniff wireless traffic and identify target networks.
The process begins by putting the wireless adapter into monitor mode. Once in this state, Airodump-ng scans the airspace, listing nearby Wi-Fi networks, their channels, encryption types, and associated clients. The attacker then selects a target network.
Capturing the Handshake: A Crucial Data Point
The key to cracking WPA/WPA2-PSK lies in obtaining the 4-way handshake. This exchange occurs when a client device (like a laptop or smartphone) connects to the WPA/WPA2 access point. The handshake is a series of packets that verifies the client's knowledge of the PSK without directly transmitting it in plain text.
Airodump-ng is used to listen for this handshake. To expedite its capture, attackers often employ a technique called deauthentication. This involves sending spoofed deauthentication frames, forcing connected clients to disconnect. When the client attempts to reconnect, the 4-way handshake is initiated, and Airodump-ng can capture it. This captured data is typically saved to a .cap or .pcap file.
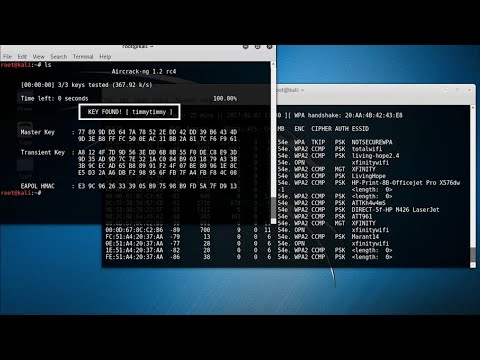
The Cracking Phase: Employing Aircrack-ng
Once the 4-way handshake is captured, the Aircrack-ng tool takes center stage. It utilizes the data from the .cap file and attempts to crack the WPA/WPA2 PSK using a dictionary file or a brute-force attack. The core principle is that Aircrack-ng will generate candidate PSKs, encrypt them using the WPA/WPA2 algorithm, and compare the resulting encrypted data with the encrypted data captured in the 4-way handshake. If they match, the candidate PSK is the actual network key.
The Fallout: Understanding Vulnerabilities and Impact
The success of such an attack hinges entirely on the strength of the chosen PSK. A weak, easily guessable key renders the WPA/WPA2 encryption practically useless. The consequences are severe:
- Unauthorized Network Access: Attackers gain entry to the internal network, bypassing perimeter firewalls.
- Data Interception: All traffic transmitted over the compromised Wi-Fi network can be sniffed and analyzed.
- Malware Propagation: The attacker can introduce malicious software onto the network, potentially spreading to other devices.
- Lateral Movement: Once inside, attackers can explore the network for further vulnerabilities and pivot to more critical systems.
- Reputational Damage: A public Wi-Fi breach can severely damage an organization's trust and credibility.
Taller Defensivo: Fortaleciendo Tu Red Wi-Fi
The threat is real, but the defenses are actionable. Negligence in securing wireless networks is a direct invitation for compromise. Here’s how to bolster your defenses:
1. Implement Robust WPA3 or WPA2-Enterprise
If your hardware supports it, migrate to WPA3. It offers significant security improvements, including stronger encryption and protection against offline dictionary attacks through Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE). For organizations, WPA2-Enterprise (or WPA3-Enterprise) is the gold standard. This uses a RADIUS server for authentication, meaning each user has unique credentials, eliminating the single point of failure inherent in PSKs. This is the professional-grade solution; anything less is an amateur gamble.
2. Strength in Passphrases: The Power of Long, Complex Keys
If using WPA2-PSK is unavoidable, choose a passphrase that is long (at least 15-20 characters), complex, and not easily guessable. Think of a memorable sentence and combine it with numbers and symbols, rather than a single word or common phrase. For example, "My CatFluffy_loves_TUNA_on_Tuesdays!" is far more robust than "Fluffy123".
3. Network Segmentation and Isolation
Isolate your guest Wi-Fi network from your internal corporate network. Use VLANs or separate access points for guest access. This ensures that even if the guest network is compromised, your sensitive internal data remains shielded. Treat guest networks as inherently untrusted environments.
4. Regular Audits and Monitoring
Conduct regular wireless security audits. Use tools to scan for rogue access points and assess the strength of your current encryption and authentication mechanisms. Implement network monitoring to detect unusual activity, such as excessive deauthentication frames or clients attempting to connect with known weak credentials.
5. Disable WPS
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) is a convenience feature that often introduces significant security risks, particularly its PIN-based authentication, which is vulnerable to brute-force attacks. If you are not using it, disable WPS on your access points.
Arsenal of the Operator/Analista
- For Network Analysis & Cracking (Ethical Testing):
- Aircrack-ng Suite: Essential for analyzing and testing Wi-Fi security.
- Wireshark: For deep packet inspection and traffic analysis.
- Kali Linux: A distribution pre-loaded with security auditing tools.
- For Network Monitoring & Defense:
- Network Monitoring Solutions (e.g., ManageEngine, PRTG): For real-time traffic analysis and anomaly detection.
- Wireless Intrusion Prevention Systems (WIPS): Dedicated hardware/software to detect and mitigate wireless threats.
- Essential Reading:
- "The Certified Wireless Security Professional (CWSP) Official Study Guide"
- "Wireshark 101: Essential Skills for Network Analysis"
Veredicto del Ingeniero: ¿Vale la pena el Riesgo Innecesario?
WPA/WPA2-PSK, when implemented with a strong passphrase, offers a reasonable baseline of security for small to medium environments. However, it is fundamentally flawed due to its reliance on a single, static key and the inherent human tendency towards weak credentials. The ease with which a 4-way handshake can be captured and subjected to offline attacks means that any network protected solely by WPA2-PSK is perpetually under siege. The transition to WPA3 or WPA2-Enterprise is not merely an upgrade; it's a necessary evolutionary step for organizations serious about securing their wireless infrastructure. Continuing to rely on weak PSKs is akin to leaving your vault door unlocked with a note saying, "Please don't rob us."
Preguntas Frecuentes
¿Es legal auditar mi propia red Wi-Fi?
Sí, auditar y probar la seguridad de tu propia red es legal y, de hecho, una práctica recomendada para identificar vulnerabilidades. Sin embargo, realizar estas pruebas en redes de las que no eres propietario o no tienes permiso explícito es ilegal.
¿Cuánto tiempo tarda en romperse una clave WPA2?
Esto varía enormemente. Una clave muy débil (ej. "password") puede romperse en minutos. Una clave fuerte (ej. 20 caracteres aleatorios) puede tardar años o incluso ser computacionalmente inviable con hardware de consumidor. La captura del handshake es el primer paso; el tiempo de cracking depende de la clave.
¿Qué es más seguro, WPA2 o WPA3?
WPA3 es significativamente más seguro que WPA2. Introduce la autenticación SAE (Similar to a handshake, but with stronger protection against offline dictionary attacks), cifrado más robusto para redes abiertas (Opportunistic Wireless Encryption - OWE), y una mayor protección para redes empresariales.
¿Puedo usar mi teléfono para auditar mi Wi-Fi?
Algunos teléfonos Android con adaptadores compatibles pueden ejecutar herramientas de monitoreo y auditoría Wi-Fi, pero las capacidades suelen ser limitadas en comparación con una estación de trabajo dedicada que ejecuta Kali Linux u otro sistema operativo de pentesting.
El Contrato: Asegura Tu Perímetro Inalámbrico
Has visto la anatomía de un ataque a redes Wi-Fi WPA/WPA2. Has comprendido las herramientas, las debilidades y las técnicas. Ahora, el contrato es contigo mismo y con la seguridad de tu infraestructura. Tu desafío es simple pero crítico: **realiza una auditoría exhaustiva de tu propia red Wi-Fi.**
- Verifica el protocolo de seguridad que estás utilizando (WPA2-PSK, WPA2-Enterprise, WPA3).
- Si usas WPA2-PSK, evalúa la fortaleza de tu passphrase. ¿Es lo suficientemente larga y compleja?
- Si tienes una red de invitados, asegúrate de que esté completamente aislada de tu red interna.
- Investiga la posibilidad de migrar a WPA2-Enterprise o WPA3.
No esperes a ser la próxima estadística en un informe de brechas. El conocimiento es poder; aplicarlo es seguridad.

No comments:
Post a Comment